Queues Preparation
Overview
While lists are a good general linear structure, you don’t always need all of the functionality and complexity of them. Today we are focused on a simpler, but vital, data structure: the queue.
Basic Learning Objectives
Before class, you should be able to:
- Explain what a queue is and how items are added and removed
- Define FIFO
Advanced Learning Objectives
After class, you should be able to:
- Explain the efficiency concerns related to implementing a queue
- Explain how a circular queue works
- Explain how a linked queue works
Readings
You should read the following:
Checks
Submit answers to the following on Moodle, given this Kotlin Queue Implementation:
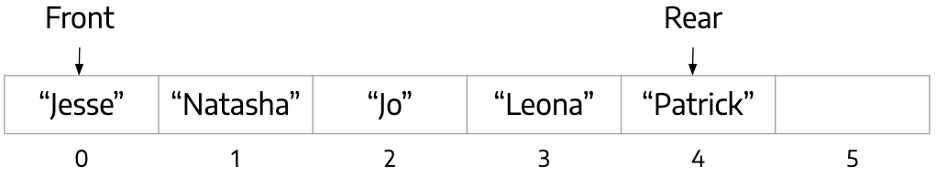
dequeue()is called on the Queue above.- What does the Queue look like now? (i.e. Which elements are in which index?)
- Which index is
frontpointing to? - Which index is rear pointing to?
enqueue("Nick")is next called on the Queue.- What does the Queue look like now? (i.e. Which elements are in which index?)
- Which index is front pointing to?
- Which index is rear pointing to?
Acknowledgements
The check questions and diagram are from Prof Jean Salac.